We all have struggled with falling or maybe staying asleep. Restless hours and counting sheep have become a part of our daily night routine. Having a good night's sleep isn't just about feeling fresh in the morning but it is also about our overall health which is equally important.
suggests that at least 7-9 hours of sleep for adults is a must. Not getting enough quality sleep can lead to various health problems, like high blood pressure and even gaining weight.
That is why people nowadays are consuming melatonin supplements to get a night of better sleep. So, What is Melatonin?
Melatonin is a hormone in your body that is produced on its own. It is like telling your body that it is time to sleep. Melatonin is a part of your body's natural way of sleeping that starts working when it gets darker.
However, there are pills as well that do the same work as melatonin in your system. These supplements claim to help you fall asleep faster and also stay asleep longer. The basic idea is to increase the level of melatonin in your body to make sure you get the best night's sleep.
Common Uses of Melatonin
Melatonin is used in various different situations, such as:
- Addressing sleep disorders to get your sleeping schedule back on track.
- Managing delayed sleep phase syndrome, which is struggling to sleep at the usual time.
- Handling sleep disorders that affect children
- Managing insomnia.
- Adapting to a different time zone and new sleep routines.
Apart from the important role melatonin plays in sleep, it also addresses various other health issues, including migraines, hypertension (high blood pressure), thrombocytopenia (low blood platelet counts), and even sunburn.
However, it's important to note that while melatonin is commonly used as a dietary supplement, it is not officially approved by the FDA for treating specific diseases or medical conditions. However, some FDA-approved medications addressing melatonin receptors are available to treat insomnia.
How Does Melatonin Work?
Melatonin is a hormone made by a small gland present right in the middle of your brain called the pineal gland. This pineal gland is controlled by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), i.e. a group of nerve cells in your hypothalamus—these cells further help in sending signals to keep your body clock in check.
During the daytime, your eye's retina absorbs light and communicates with the SCN to send signals to the pineal gland to stop producing melatonin. This helps you stay alert and awake during the day. But when it gets darker, the SCN flips things up. It tells the pineal gland to start producing melatonin.
As melatonin levels rise, your body gets ready for sleep—body temperature drops, blood pressure lowers, and it even calms down the SCN, signaling that it's time to hit the sack.
How Long Does It Take For Melatonin to Work?
The impact of melatonin supplements varies from person to person. Some might start feeling sleepy an hour after taking it, while others might experience tiredness in just 10 to 15 minutes. Despite these differences, the body quickly absorbs melatonin, and most people generally feel its full effects within the first hour.
Typically, melatonin supplements are quickly released into the bloodstream right after consumption. However, there are also formulations designed for extended release. With these, small amounts of melatonin gradually enter the bloodstream over time. This type of melatonin is meant to imitate the body's natural melatonin production, which happens throughout the night.
The Ideal Time to Consume Melatonin to Help You Sleep
The best possible time to consume melatonin completely differs from person to person. It's generally recommended to take melatonin about 30-60 minutes before bedtime. It is clinically proven that low doses, specifically 2mg or less, are generally considered safe.
It is recommended to begin melatonin dosage with small amounts to know its effects better and then gradually increase if necessary. Here's a suggested guideline based on age, but it is always advisable to consult with your doctor before consuming the same:
- 3-5 years: 1 to 2 mg
- 6-12 years: 2 to 3 mg
- Over age 13: up to 5 mg
You can also adjust the dosage gradually based on your needs. Remember, consuming melatonin at or after your bedtime can lead to daytime drowsiness and make you feel lethargic.
How Long Does Melatonin Last On Your Body?
Melatonin doesn't long haul in your body. It usually stays in for 5 hours unless you've taken slow-release melatonin. During this time, you might avoid doing tasks like driving or using heavy machinery as you might start to feel sleepy during this period.
Different things affect the way melatonin works in your system, such as:
- Age: The older you are, the longer melatonin might stay in your body. This is because the metabolism slows down with age.
- Body Size: A bigger person, weighing more than 250 pounds might not feel much effect with a smaller amount of melatonin doze.
- Light Exposure: Exposure to light, especially the blue light from devices, can mess with melatonin levels.
- Caffeine: Drinking coffee or consuming other products containing caffeine can affect the working process of melatonin.
- Tobacco: Smoking also affects the way melatonin works in your body.
- Other Medicines: If you are under certain medications for things like diabetes, blood pressure, hypertension, or immunosuppressants, they might change the working structure of melatonin in your system.
Now, if you take melatonin at the right time, you might not feel sleepy the next day. It depends on whether you're taking regular melatonin or the extended-release kind.
Does Melatonin Wear Off Fast From Your Body?
The amount of melatonin consumed is always equal to the hours it's gonna last. Generally, it takes around 4 to 8 hours to wear off. Therefore, it is ideal to consume melatonin at least 20-30 minutes before going to bed. It is best if you can consume it an hour before your bedtime.
It is always recommended to take small amounts of melatonin at the beginning so that it can wear off quickly without leading to any significant side effects.
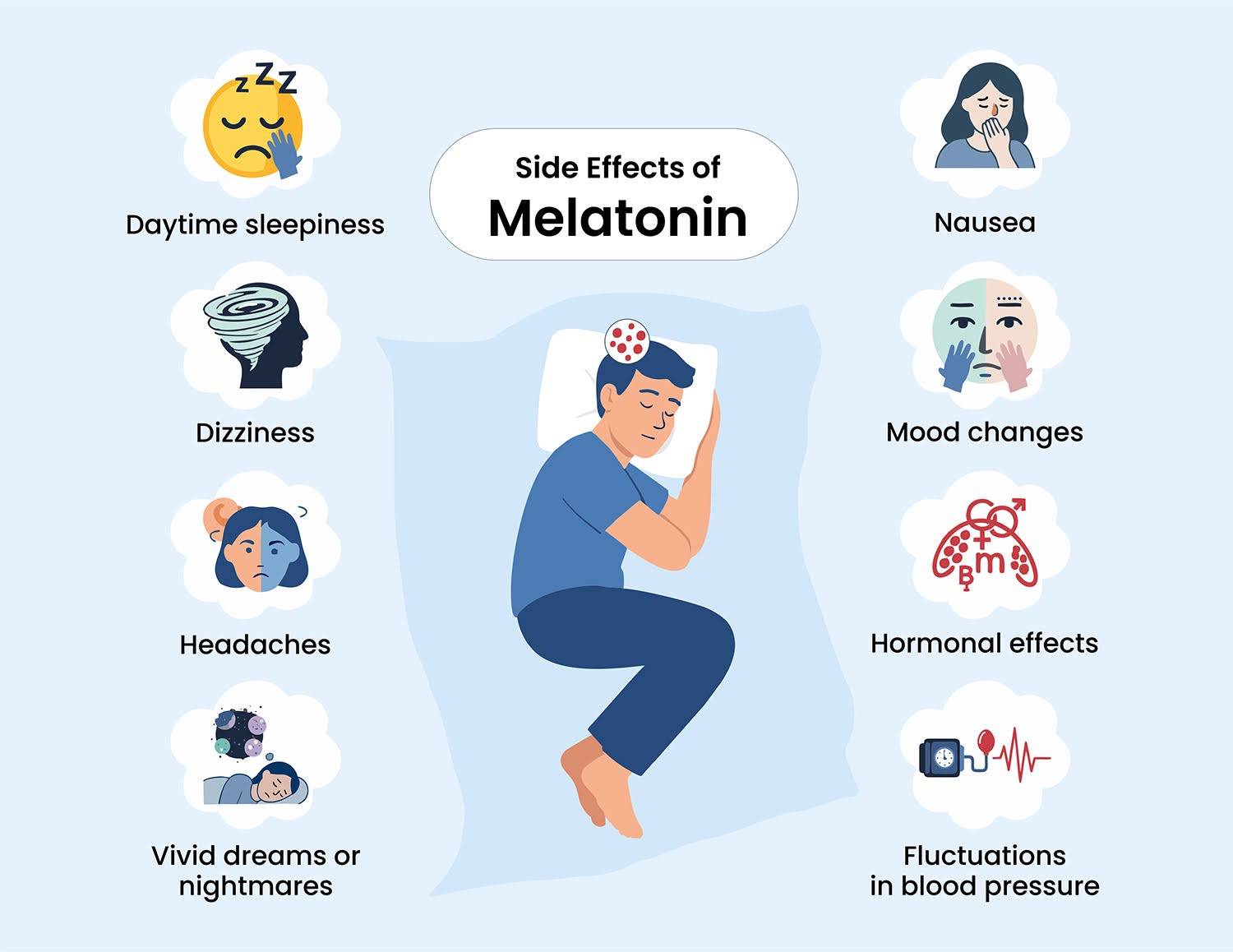
The Significant Side Effects of Melatonin Consumption
Limited melatonin consumption is normally safe. The main purpose of it is to make you feel sleepy, which is why most people use it.
However, like any other thing, there are side effects to this as well. The common ones include the following:
- headaches,
- nausea, and
- feeling groggy.
Other, side effects that are more likely to happen if you take too much melatonin are:
- discomfort,
- joint pain,
- neck and shoulder pain,
- back pain
- trouble sleeping,
- seizures,
- Anxiety,
- stress,
- irritability,
- depression,
- nightmares, and
- low blood pressure.
Also, if you're pregnant or breastfeeding, have kidney or heart disease, or deal with depression, it's a good idea to avoid melatonin.
In such cases, you can follow good sleep hygiene, different sleeping positions, or even get yourself comfortable and expert-recommended pillows. This will not only help you sleep better but also help you cope with your shoulder, back, or neck pain, especially if you are pregnant.
Final Thought
Melatonin is like a sleeping companion that relatively lasts for a shorter period of time in your body, offering you much-needed sleep. However, understanding its pros and cons and making smart choices can help you keep away from its harmful effects.
Remember, consulting your doctor before making any decision is a wise choice to make.













