If you are suffering from lower back pain frequently, then you are not alone. It might sound unreal, but lower back pain is widespread in today’s day and age. According to the American Chiropractic Association, in the United States, it's estimated that 31 million Americans experience lower back pain at any given time. A study by Global Burden of Disease states that lower back pain is the leading cause of disability, affecting over 540 million people.
While lower back pain can affect people of all ages, it becomes more common as people age. National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke studies show that prevalence increases significantly after age 30 and peaks between ages 45 and 64.
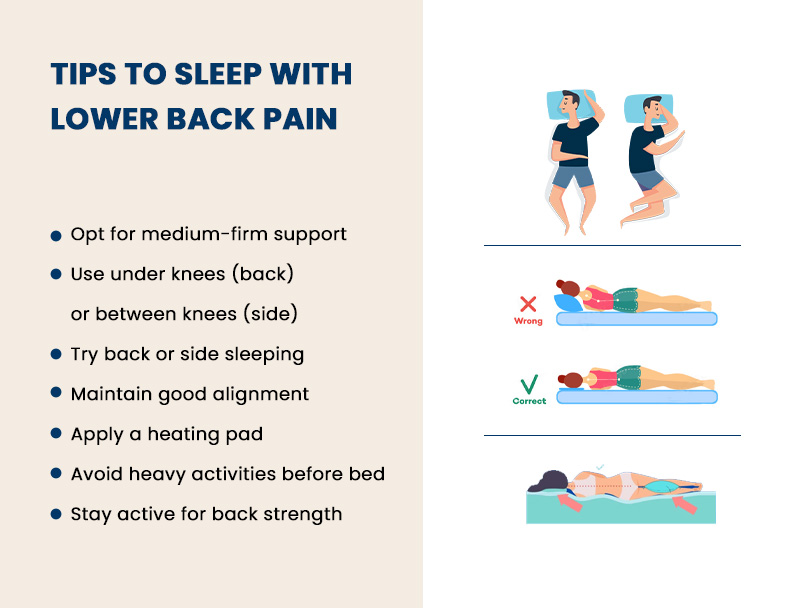
Improving your sleeping position is one simple and effective way to alleviate lower back pain. We will discuss the best sleeping positions for lower back pain and how they can relieve and promote better spinal health.
Primary Causes of Lower Back Pain
To understand and manage back pain, it is vital to know the common cause:
1. Muscle or ligament strain
It is one of the most common causes of back pain. It can happen due to improper lifting of heavy objects, sudden awkward movements, or poor posture over time. The muscles and ligaments in the back can become strained, causing pain and discomfort. This type of back pain can be relieved with rest, proper stretching, and avoiding strenuous activities.
2. Herniated or bulging disc
Another major cause of back pain is a herniated or bulging disc. The discs between the vertebrae can bulge or rupture, putting pressure on nerves and causing pain. This can happen due to injury or degenerative changes. In some cases, the pain can be severe and may require medical treatment, such as physical therapy or surgery.
3. Degenerative Disc Disease
As people age, it is typical for the discs in the back to degenerate, leading to back pain. This is known as degenerative disc disease. The discs lose fluid and flexibility, resulting in pain and stiffness. This condition may also accompany other age-related changes, such as osteoarthritis.
4. Spinal stenosis
It is another common cause of back pain, especially in older adults. It occurs when the spinal canal narrows, putting pressure on the spinal cord and nerves. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs.
5. Skeletal irregularities
Irregularities like scoliosis or lordosis can also lead to back pain. These conditions involve abnormal curvature of the spine, which can cause muscle imbalances and pain.
6. Osteoarthritis
It is a condition where the cartilage in the joints breaks down and can also cause back pain. This can affect the lower back, resulting in pain and stiffness.
7. Osteoporosis
It is a condition where bones become porous and brittle, leading to back pain. As the bones weaken, they are more prone to fractures, particularly in the spine. These compression fractures can cause severe pain and require medical treatment.
8. Traumatic injuries
Back pain can result from accidents, falls, or sports injuries. These injuries can result in fractures, sprains, or strains, which can cause pain and discomfort.
Which Sleeping Position Triggers Lower Back Pain?

Among the standard positions, sleeping on your stomach (prone position) tends to be the most likely to trigger or exacerbate lower back pain. Here’s why:
Spinal Misalignment: When you sleep on your stomach, your spine is forced into an unnatural curve. This position can strain the muscles and ligaments in your lower back, leading to discomfort and pain.
Neck Strain: Sleeping on your stomach requires you to turn your head to one side or the other to breathe, which can strain your neck muscles and exacerbate any existing neck or upper back issues.
Pressure on Organs: Stomach sleeping can also put pressure on your organs and cause issues with digestion and breathing, though this is less related to lower back pain.
Lack of Support: Many people who sleep on their stomachs do not use a pillow under their hips, which can further increase the strain on the lower back by causing it to arch excessively.
For these reasons, sleeping on your stomach is generally not recommended if you have lower back pain or want to prevent it. Instead, sleeping on your back or side with proper support and spine alignment is typically better for reducing lower back pain and promoting overall spinal health.
Best Sleeping Positions to Prevent Lower Back Pain
Here's a breakdown of each sleeping position and how to relieve lower back pain:
Sleep on Your Side with a Pillow Between Your Knees
- Lie on your side
- Place a pillow between your knees.
- Keep your knees slightly bent.
- Ensure your spine remains straight.
How does it help?
This position helps align your spine, pelvis, and hips, reducing stress on your lower back. The pillow between your knees prevents your upper leg from pulling your spine out of alignment, thus preventing strain on your lower back muscles.
Sleep on Your Side in the Fetal Position
- Curl your torso into a fetal position by lying on your side
- Tuck your knees toward your chest.
- Keep your back slightly curved.
How does it help?
The fetal position can help open up your spine's joints and reduce pressure. Reducing spinal bending may also alleviate discomfort from herniated discs.
Sleep on Your Stomach with a Pillow Under Your Abdomen
- Lie face down on your stomach
- Place a pillow under your abdomen and pelvis.
- Keep your neck in a neutral position.
How does it help?
Placing a pillow under your abdomen can help maintain the natural curve of your lower spine, reducing the strain that sleeping on your stomach can cause. It can also alleviate pressure on your neck and upper back.
Sleep on Your Back with a Pillow Under Your Knees
- Lie on your back
- Place a pillow under your knees.
- Keep your spine neutral
- Maintain the natural curve of your lower back.
How does it help?
This position evenly distributes your weight and supports your spine's natural curvature. The pillow under your knees helps reduce pressure on your lower back and promotes muscle relaxation.
Sleep on Your Back in a Reclined Position
- Sleep on your back in a semi-upright position
- Use an adjustable bed or reclining chair.
- Support your head and keep your knees slightly elevated.
How does it help?
Sleeping in a reclined position can reduce pressure on your lower back by supporting the spine and allowing it to rest in a more natural alignment. It can be particularly beneficial for people with spinal stenosis or degenerative disc disease.
What Pillow is Best for Lower Back Pain?
Selecting the best pillow for lower back pain depends significantly on your sleeping position and personal comfort preferences. Here's a tailored guide for different types of sleepers:
1. Side Sleepers
Side sleepers often benefit from a pillow that maintains proper spinal alignment by filling the space between the head and the mattress. Look for a firm or medium-firm pillow with a higher loft to adequately support the head and neck. Memory foam pillows are ideal as they contour to the shape of your head and neck, providing personalized support throughout the night. This combination helps relieve pressure points and can be considered one of the best pillows for lower back pain for side sleepers.
2. Back Sleepers
Back sleepers need a pillow supporting the cervical spine's natural curve while ensuring the head is not too high or too low. A medium loft pillow with medium firmness is typically recommended. Memory foam or latex pillows conform to the neck and head contours, providing support without excessive elevation. This support helps maintain proper spinal alignment and is quite effective for back sleepers.
3. Stomach Sleepers
Stomach sleepers should opt for a thinner, softer pillow to prevent the neck from being strained unnaturally. Too much loft can strain the neck and contribute to lower back pain. Look for a smooth, low loft pillow that keeps the head aligned with the spine. Down or down alternative pillows often provide the necessary softness while still offering some support. This type of pillow helps minimize strain on the lower back and is perfect for stomach sleepers.
4. Combination Sleepers
Combination sleepers who switch positions at night need a versatile pillow accommodating various sleeping styles. Adjustable loft pillows or those made from shredded memory foam or latex are suitable options. These pillows can be fluffed or molded to provide the proper support and comfort regardless of how you sleep. They offer adaptability and support, making them exceptionally comfortable for combination sleepers.
What Mattress is Best for Lower Back Pain?
Choosing the best mattress for lower back pain depends mainly on your sleeping position and personal preferences. Here’s a breakdown for different types of sleepers:
1. Side Sleepers
Side sleepers typically benefit from mattresses that provide contouring support to relieve pressure points, especially around the hips and shoulders. A medium- to medium-soft mattress with good support can help align the spine and alleviate lower back pain.
Look for memory foam or hybrid mattresses that offer adequate cushioning without compromising support.
2. Back Sleepers
Back sleepers need a mattress that supports the spine's natural curve, particularly in the lumbar region. A medium-firm mattress is often recommended as it provides enough support to keep the spine aligned adequately while offering sufficient cushioning for comfort.
Look for materials like memory foam or latex, which contour to the body's shape while supporting the lower back. This combination helps distribute weight evenly and reduces pressure points.
3. Stomach Sleepers
Stomach sleepers require a firmer mattress to prevent the lower back from sinking too deeply, which can lead to misalignment of the spine. A medium-firm to firm mattress helps maintain a neutral spine position and supports the hips and abdomen.
Look for mattresses with supportive coils or dense foam that provide stable support without excessive sinking. This firmness level ensures proper spinal alignment and reduces the risk of lower back pain.
4. Combination Sleepers
Combination sleepers who switch positions at night should consider a versatile mattress that accommodates various sleeping styles. A medium-firm mattress with responsive materials like latex or hybrid constructions is a good choice.
These mattresses offer support and comfort, adjusting quickly to changes in sleeping positions. Maintaining spinal alignment throughout the night helps alleviate lower back pain.
When to Seek Medical Care?
It's crucial to seek medical care for lower back pain under several circumstances: if the pain is severe and unresponsive to over-the-counter treatments; if it radiates down the legs accompanied by numbness, tingling, or weakness; if it persists for more than a few weeks despite rest and medications; if you have a history of cancer, osteoporosis, or recent trauma coupled with new onset of back pain.
If there is fever accompanying the pain, if there's loss of bladder or bowel control, or if the pain follows significant trauma. Prompt medical attention ensures proper diagnosis and treatment, particularly to address underlying conditions that may require specialized care to prevent complications and alleviate symptoms effectively.












